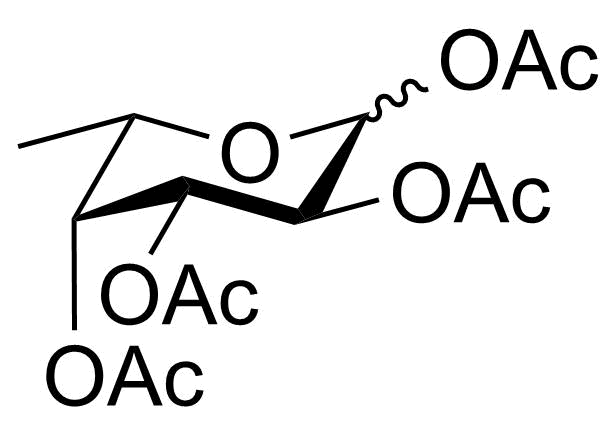
P-Fuc
Control compound for experiments utilizing fucose derivatives
| Product ID: | SV3768 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms: | Ac4Fuc |
| Tags: | Control compound, Fucose |
| Product | Price | Estimated Shipping Time | Purchase |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-Fuc - 1 mg | €60.00 | 1-3 days | |
| P-Fuc - 5 mg | €90.00 | 1-3 days | |
| P-Fuc - 10 mg | €125.00 | 1-3 days | |
| P-Fuc - 25 mg | €225.00 | 1-3 days | |
| P-Fuc - 100 mg | €525.00 | 1-3 days |
Product information
-
Function
P-Fuc is a control compound for labeling/inhibition experiments utilizing acetylated fucose derivatives such as P-Fuc2F, P-Fuc6Az, P-Fuc7Alk.
-
Mode of action
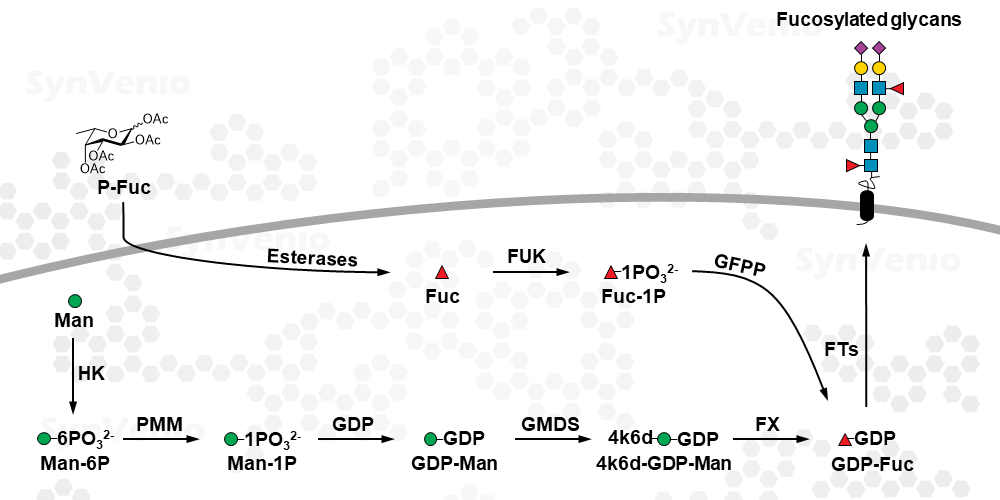
P-Fuc is taken up by cells via passive diffusion because this compound contains O-acetyl (OAc) groups. These groups make the molecule more lipophilic so that it can passively diffuse over mammalian cell membranes. Inside cells, these O-acetyl groups are removed via non-specific esterase releasing fucose and acetic acid. It is possible that at high concentrations, the released acetic acid or the partially acetylated intermediates are toxic. In addition, at high concentrations, non-specific reactions of acetylated precursors and cysteine residues have been observed.1 At low µM concentrations, these effects are likely negligible but it is advisable to use a control compounds such as P-Fuc. Finally, these lipophilic precursors may be used to boost intracellular monosaccharide levels. This has been demonstrated for cell permeable neuraminic acid derivative P-Neu5Ac.2
-
Applications
Control compound for labeling/inhibition experiments utilizing acetylated fucose derivatives (P-Fuc6Az, P-Fuc7Alk, P-Fuc2F). Potentially as a cell permeable derivative to boost intracellular fucose levels.
-
Handling
P-Fuc is soluble in a mixture of DMSO and PBS and is added to cell culture from a stock solution.
-
Chemical Information
CAS No.: 64913-16-2
SMILES: C[C@H]1[C@@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@H](OC(C)=O)[C@H](OC(C)=O)C(OC(C)=O)O1
Chemical formula: C14H20O9
Molecular weight: 332.30
Purity: > 95%
Identity: 1H NMR
Shipping temperature: 20°C
Storage temperature: 20°C
Recommended Products
| Name |
|---|
| Neu5Ac9Az |
| P-GalNAc6Az |
| P-Neu5Ac3F |
| XylPNP |
| P-ManNDAz |
Calculator
Dissolve the required mass in your desired stock volume.
Dilute the required volume of your stock solution to the desired final volume.